Shedding Light on Fatty Liver
In a country where almost 70% people are diagnosed with fatty liver, knowing about the issue and its preventive measures is really important. Some excerpts from an interview with Dr. T. Laxmi Kanth, MS, FAIS, Dip. LS (France), FIGS (Japan), Sr. Consultant Surgical Gastroenterology, Laparoscopic, Bariatric and Robotic Surgeon , KIMS Hospitals, Secunderbad . For Appointment Call : +91 9704405454 .
.jpg)
What is fatty liver?
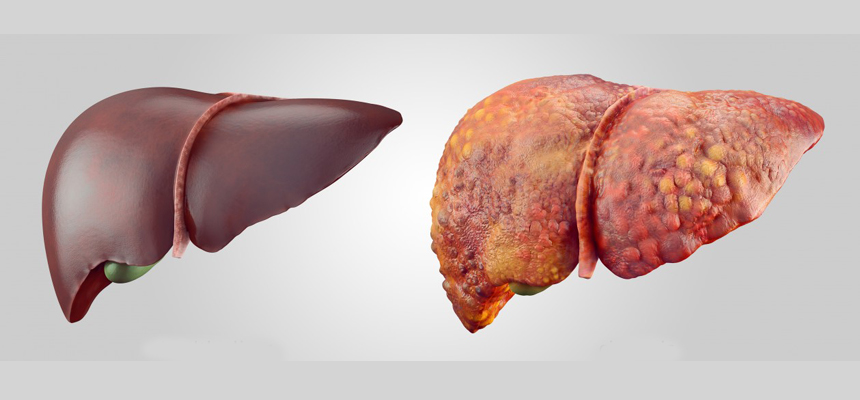
Known as Hepatic Steatosis, this is a condition when fat gets built up in the liver. It is alright to have some amount of fat but excess may result in a situation of fatty liver. Excess fat becomes a hindrance in the normal functioning of liver. The job of a liver is to filter what you eat and drink. It removes a harmful substances from the food and water and supplies the nutrients to the blood and heart. Harmful substances or fatty substances when get accumulated and the liver and constitutes for 5 to 10% of liver’s weight then fatty liver is said to have occurred. Other harmful effect of fatty liver is that the organ starts losing its ability to heal itself. The liver has an amazing regenerative property that it can regrow itself if some part gets damaged. In the situation of fatty liver this regenerative property slows down, as a result the liver is not able to build itself. Accordingly, it is not able to function properly and fat gets accumulated in the liver. Excess of fat may result in permanent scarring of liver known as cirrhosis.
What are the symptoms of fatty liver?
Till date, no specific symptoms have been associated with fatty liver. People usually experience fatigue, mild abdominal pain and reduced appetite. Other symptoms that can be seen in people suffering from fatty liver are rapid weight loss, physical weakness and confusion. In cases where fatty liver becomes cirrhosis and leads to liver failure, the symptoms start getting severe. They include presence of large fluid filled abdominal, jaundice, easy bleeding and confusion.
According to a research by American Liver Foundation about 10 to 20% of Americans are a target of fatty liver especially those aged between 40 to 60 years. These patients have been diagnosed with fatty liver without causing cirrhosis or inflammation of the liver.
What are the causes of fatty liver?
Heavy alcoholism is named number one reason leading to fatty liver. The presence of excess fat and not metabolizing this fat fast enough, the presence of sugar and alcohol tend to worsen this condition. High fat and high sugar can contribute to increase in the fat of liver. This may lead to acute cirrhosis and ultimately liver failure. Once the liver has been diagnosed as failed, the survival chances are limited maximum for 2 years. People suffering from diabetes and obesity are also prone to fatty liver. Other situations like hyperlipidemia (high fat in blood), generic inheritance and rapid weight loss also lead to fatty liver.
What are the types of fatty liver?
There are two types of fatty liver- alcoholic fatty liver and nonalcoholic fatty liver.
In non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), the liver cannot break up the fat in the body fast enough. As a result, fat gets accumulated in liver. NAFLD is said to have occurred when more than 10% of liver is made up of fat.
Alcohol has a direct impact on liver and with its excess consumption, the liver it is not able to break down fat and sugar fast enough. If drinks are totally prohibited, the excess fat of liver is likely to subside. If even more alcohol is consumed after fatty liver is diagnosed, cirrhosis will occur in no time.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) occurs when excess fat causes the liver to swell. When original cause is not alcohol, the condition is NASH. Symptoms include loss of appetite, state of nauseousness, vague abdominal pain and jaundice. When alcohol is the reason it is called alcoholic steatohepatitis. If proper care is not administered to the patient, there are strong chances of liver failure and death.
Acute fatty liver failure rarely occurs in pregnant women but it's dangers to the pregnancy cannot be ignored. Symptoms occur in third trimester with onset of nausea, vomiting, jaundice and general malaise. The condition gets better post pregnancy and does not have any lasting effects.
Who is at risk of fatty liver?
Since fatty liver is excess fat in liver, if you are overweight or obese chances of fatty liver or higher. Diabetic patients with type 2 diabetes are also at high risk. Diet rich in chlorine has shown lower risk of fatty liver disease. Other than high alcohol consumption, the reasons for fatty liver are high doses of acetaminophen (Tylenol), high cholesterol, high triglyceride levels, malnutrition and metabolic syndrome.
How can fatty liver be diagnosed?
There are various ways fatty liver can be diagnosed
![]() Physical Examination: The doctors can find this condition by examining your liver. Inflamed or enlarged liver is an indication of fatty liver. Discuss your eating habits, disease history, alcohol, medication and supplementary regime.
Physical Examination: The doctors can find this condition by examining your liver. Inflamed or enlarged liver is an indication of fatty liver. Discuss your eating habits, disease history, alcohol, medication and supplementary regime.
![]() Blood Test: This method cannot guarantee that the high amount of liver enzymes found in blood test are due to fatty liver. Further tests are required to confirm fatty liver.
Blood Test: This method cannot guarantee that the high amount of liver enzymes found in blood test are due to fatty liver. Further tests are required to confirm fatty liver.
![]() Imaging: Ultrasound can be used for fat detection in the liver. Other procedures like CT scan or MRI can be vouched for. Fibroscan can also be administered to the patient. In this technique, sound waves are used to determine liver’s density of fat and nonfat regions.
Imaging: Ultrasound can be used for fat detection in the liver. Other procedures like CT scan or MRI can be vouched for. Fibroscan can also be administered to the patient. In this technique, sound waves are used to determine liver’s density of fat and nonfat regions.
![]() Liver Biopsy: In this method a needle is inserted in the liver and a tissue of liver is extracted for scan. This is the sure shot way to see whether the liver has excess or moderate fat cells. It can also determine the cause.
Liver Biopsy: In this method a needle is inserted in the liver and a tissue of liver is extracted for scan. This is the sure shot way to see whether the liver has excess or moderate fat cells. It can also determine the cause.
How to treat fatty liver?
No particular medication or surgery claims to alleviate fatty liver totally. Some recommendations by doctors in case of this scenario are:
![]() Banishing alcohol
Banishing alcohol
![]() Keeping cholesterol and sugar under check
Keeping cholesterol and sugar under check
![]() Maintaining healthy weight
Maintaining healthy weight
![]() Increased physical activity to metabolize sugar and fat
Increased physical activity to metabolize sugar and fat
![]() Consume fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains and replace red meat with lean white meat.
Consume fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains and replace red meat with lean white meat.
What is the long term impact of fatty liver?
Not necessarily all fatty liver turn into cirrhosis or liver failure. Precaution is better than cure. Keeping a watchful eye on high cholesterol, sugar and obesity can reverse fatty level scenario.
If fatty liver has progressed to cirrhosis, it can rapidly lead to liver failure and death. Hence monitoring is vital when diagnosed with such a situation.
How to prevent fatty liver disease?
Keeping your liver in good health is prime way to keep liver diseases at bay. According to Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), consuming alcoholic beverages in moderation can reduce fatty liver to a great extent. Exercising 30 minutes a day can help you maintain a healthy weight.

 Disclaimer: Welthi.com does not guarantee any specific results as a result of the procedures mentioned here, and the results may vary from person to person.
Disclaimer: Welthi.com does not guarantee any specific results as a result of the procedures mentioned here, and the results may vary from person to person.